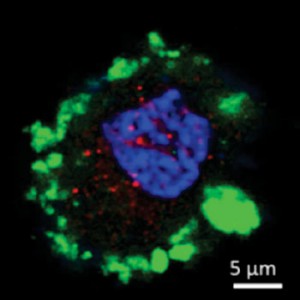
Genetically Engineered Lactobacilli Cure Diabetes in Rat Model
A novel concept for treating diabetes was demonstrated by feeding diabetic rats a diet containing human lactobacilli that had been genetically engineered to secrete the

A novel concept for treating diabetes was demonstrated by feeding diabetic rats a diet containing human lactobacilli that had been genetically engineered to secrete the

The vicious cycle of Ebola infection does not end with the death of a victim. According to researchers with the National Institutes of Health (NIH),

Jews have a genetic predisposition to lymphoma, and due to Israel’s size, much of the population lives near agricultural areas and is exposed to pesticides
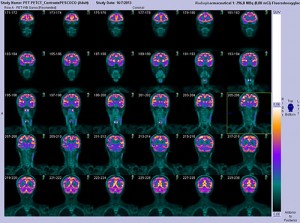
Researchers at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) in Toronto have found a possible link between inflammation in the brain and clinical depression.
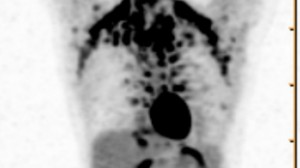
The stimulation of so-called brown fat the energy-burning kind is thought to be a potential therapeutic target for obesity. In a study published in Cell Metabolism

For many years, researchers have studied the transcription factor MYC, which promotes cell proliferation and is overexpressed in most human cancers. But MYC is also

One of the biggest concerns about genetically modified organisms (GMOs) is that they can infiltrate wild populations and spread their altered genes among naturally occurring

An international research team reports that a common gut microbe might curb the risk in women of developing multiple sclerosis. The scientists, from Australia and
A growing body of research suggests that the most common cause of dementia in older people is a mix of vascular and Alzheimer’s-related brain abnormalities,

A growing body of research suggests that the most common cause of dementia in older people is a mix of vascular and Alzheimer’s-related brain abnormalities,

Mammalian hosts fight gut infections in part by releasing antimicrobial peptides that disrupt bacterial membranes. But it has been unclear how beneficial microbes survive the

Many of the most widely used antibiotics have come out of the dirt. Penicillin came from Penicillium, a fungus found in soil, and vancomycin came

A drug called fexaramine triggers a physiological reaction in mice akin to what happens after the animals eat a big meal: releasing bile acids into

Decades of epidemiological data demonstrate that men have higher overall cancer rates than women. This difference in risk is more than four-fold for some types

Up to 5 percent of the antibodies circulating in the blood of healthy adults are directed against the carbohydrate antigen Galα1-3Galb1-4GlcNAc-R, also known as α-gal.

The brain the most exalted and enigmatic of organs, which is closed off from the rest of the body by a largely impermeable barrier could

Locking lips spreads more than just love. A healthy dose of microbes are also swapped between kissing couples, according to a study published today (November

Scientists at the Harvard Stem Cell Institute at Massachusetts General and Boston Children’s hospitals say that a novel gene editing method has been used to
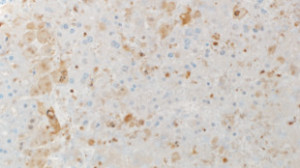
Researchers investigating host responses to Ebola have long faced a significant disadvantage: the virus kills conventional lab mice, but does not produce the hemorrhagic fever
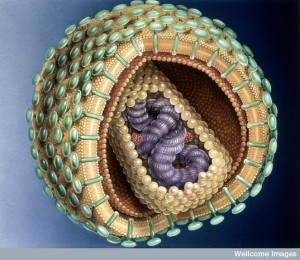
HIV’s envelope protein (Env) coats virus particles and allows HIV to enter host cells. HIV entry is highly dynamic. Env proteins work in groups of

HIV’s envelope protein (Env) coats virus particles and allows HIV to enter host cells. HIV entry is highly dynamic. Env proteins work in groups of
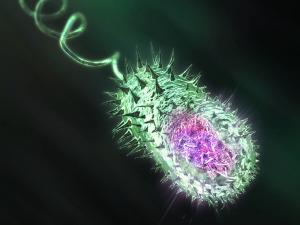
Cholera kills more than 100,000 people yearly and results from consuming food or water contaminated with Vibrio cholerae. The bacterium only expresses virulence factors, proteins

Researchers at Northwestern Medicine say they have developed the first blood test to diagnose major depression in adults. The assay, which works by measuring the levels of
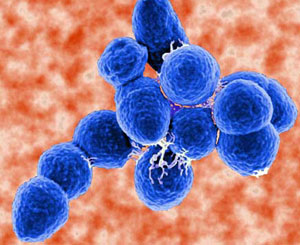
Since the 1960s, group B streptococci (GBS) have lost genetic diversity, yet they cause more virulent neonatal infections and show high rates of tetracycline resistance.

Since the 1960s, group B streptococci (GBS) have lost genetic diversity, yet they cause more virulent neonatal infections and show high rates of tetracycline resistance.
Created by ePubSystems. Contact Us for similar site for your university or institute.