Highlights
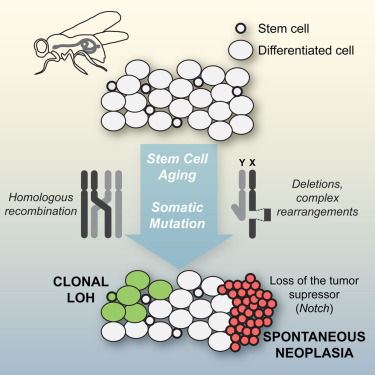
- •The aging Drosophila intestine is genetically mosaic
- •Somatic recombination, genomic deletions, and rearrangements occur in aging ISCs
- •Somatic inactivation of the tumor-suppressor Notch causes male-specific neoplasia
Summary
Adult stem cells may acquire mutations that modify cellular behavior, leading to functional declines in homeostasis or providing a competitive advantage resulting in premalignancy. However, the frequency, phenotypic impact, and mechanisms underlying spontaneous mutagenesis during aging are unclear. Here, we report two mechanisms of genome instability in adult Drosophila intestinal stem cells (ISCs) that cause phenotypic alterations in the aging intestine. First, we found frequent loss of heterozygosity arising from mitotic homologous recombination in ISCs that results in genetic mosaicism. Second, somatic deletion of DNA sequences and large structural rearrangements, resembling those described in cancers and congenital diseases, frequently result in gene inactivation. Such modifications induced somatic inactivation of the X-linked tumor suppressor Notch in ISCs, leading to spontaneous neoplasias in wild-type males. Together, our findings reveal frequent genomic modification in adult stem cells and show that somatic genetic mosaicism has important functional consequences on aging tissues.