Highlights
- •Tumor cell metabolic flexibility enables glucose-independent cell proliferation
- •PCK2 helps generate glycolytic intermediates under low-glucose conditions
- •PCK2 expression is regulated by glucose and required for in vivo tumor growth
- •PCK2 expression is elevated in non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC)
Summary
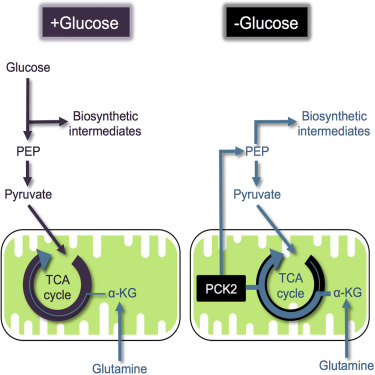
Cancer cells adapt metabolically to proliferate under nutrient limitation. Here we used combined transcriptional-metabolomic network analysis to identify metabolic pathways that support glucose-independent tumor cell proliferation. We found that glucose deprivation stimulated re-wiring of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and early steps of gluconeogenesis to promote glucose-independent cell proliferation. Glucose limitation promoted the production of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) from glutamine via the activity of mitochondrial PEP-carboxykinase (PCK2). Under these conditions, glutamine-derived PEP was used to fuel biosynthetic pathways normally sustained by glucose, including serine and purine biosynthesis. PCK2 expression was required to maintain tumor cell proliferation under limited-glucose conditions in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. Elevated PCK2 expression is observed in several human tumor types and enriched in tumor tissue from non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Our results define a role for PCK2 in cancer cell metabolic reprogramming that promotes glucose-independent cell growth and metabolic stress resistance in human tumors.