Significance
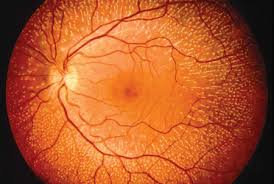
Alu elements, comprising more than 10% of the human genome, propagate via retrotransposition. This genomic expansion requires enzymatic activity of L1 that reverse transcribes Alu RNA into Alu cDNA in the nucleus. We report Alu also undergoes L1-mediated reverse transcription via self-priming in the cytoplasm independent of retrotransposition, providing evidence of human DNA synthesis in this cellular compartment. This newly discovered shunt molecule in the Alu replication cycle also induces death of the retinal pigmented epithelium, a hallmark of atrophic age-related macular degeneration. A Big Data Archeology analysis of multiple health insurance databases reveals that use of FDA-approved nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors is associated with protection against macular degeneration, identifying a repurposing candidate for this blinding disease.
Abstract
Alu retroelements propagate via retrotransposition by hijacking long interspersed nuclear element-1 (L1) reverse transcriptase (RT) and endonuclease activities. Reverse transcription of Alu RNA into complementary DNA (cDNA) is presumed to occur exclusively in the nucleus at the genomic integration site. Whether Alu cDNA is synthesized independently of genomic integration is unknown. Alu RNA promotes retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) death in geographic atrophy, an untreatable type of age-related macular degeneration. We report that Alu RNA-induced RPE degeneration is mediated via cytoplasmic L1–reverse-transcribed Alu cDNA independently of retrotransposition. Alu RNA did not induce cDNA production or RPE degeneration in L1-inhibited animals or human cells. Alu reverse transcription can be initiated in the cytoplasm via self-priming of Alu RNA. In four health insurance databases, use of nucleoside RT inhibitors was associated with reduced risk of developing atrophic macular degeneration (pooled adjusted hazard ratio, 0.616; 95% confidence interval, 0.493–0.770), thus identifying inhibitors of this Alu replication cycle shunt as potential therapies for a major cause of blindness.