Highlights
- •During viral infection, inflammatory cytokines induce aerobic glycolysis in NK cells
- •Ldha expression is critical for clonal expansion of host-protective anti-viral NK and CD8+ T cells
- •LDHA facilitates NK cell-activating receptor signaling and effector function
- •NK cells rely on LDHA for their elimination of tumors
Summary
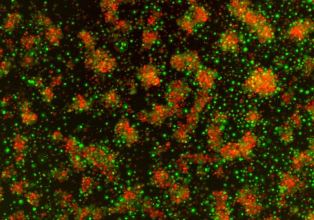
Natural killer (NK) cells are cytotoxic lymphocytes capable of rapid cytotoxicity, cytokine secretion, and clonal expansion. To sustain such energetically demanding processes, NK cells must increase their metabolic capacity upon activation. However, little is known about the metabolic requirements specific to NK cells in vivo. To gain greater insight, we investigated the role of aerobic glycolysis in NK cell function and demonstrate that their glycolytic rate increases rapidly following viral infection and inflammation, prior to that of CD8+ T cells. NK cell-specific deletion of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) reveals that activated NK cells rely on this enzyme for both effector function and clonal proliferation, with the latter being shared with T cells. As a result, LDHA-deficient NK cells are defective in their anti-viral and anti-tumor protection. These findings suggest that aerobic glycolysis is a hallmark of NK cell activation that is key to their function….