Repairing the nuclear pore in ALS
The majority of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) cases are of unknown origin (sporadic, sALS). The nuclear pore complex (NPC) has been involved in familial ALS (fALS); whether and how it plays a role also in sALS remains to be elucidated. Now, Coyne et al. used human tissue and induced pluripotent stem cell–derived motor neurons from patients with fALS and sALS to show that the protein CHMP7, previously shown to be involved in NPC homeostasis in yeast, was increased in both ALS subtypes. Antisense oligonucleotide targeting CHMP7 reduced NPC and TDP-43 abnormalities and promoted neuronal survival, suggesting that CHMP7 is a potential target for treating both sALS and fALS.
Abstract
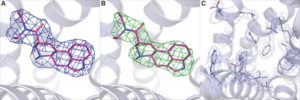
Alterations in the components [nucleoporins (Nups)] and function of the nuclear pore complex (NPC) have been implicated as contributors to the pathogenesis of genetic forms of neurodegeneration including C9orf72 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/frontotemporal dementia (ALS/FTD). We hypothesized that Nup alterations and the consequential loss of NPC function may lie upstream of TDP-43 dysfunction and mislocalization widely observed in ALS, FTD, and related neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we provide evidence that CHMP7, a critical mediator of NPC quality control, is increased in nuclei of C9orf72 and sporadic ALS induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)–derived spinal neurons (iPSNs) and postmortem human motor cortex before the emergence of Nup alterations. Inhibiting the nuclear export of CHMP7 triggered Nup reduction and TDP-43 dysfunction and pathology in human neurons. Knockdown of CHMP7 alleviated disease-associated Nup alterations, deficits in Ran GTPase localization, defects in TDP-43–associated mRNA expression, and downstream glutamate-induced neuronal death. Thus, our data support a role for altered CHMP7-mediated Nup homeostasis as a prominent initiating pathological mechanism for familial and sporadic ALS and highlight the potential for CHMP7 as therapeutic target.