MSL2 ensures biallelic gene expression in mammals
Abstract In diploid organisms, biallelic gene expression enables the production of adequate levels of mRNA1,2. This is essential for haploinsufficient genes, which require biallelic expression

Abstract In diploid organisms, biallelic gene expression enables the production of adequate levels of mRNA1,2. This is essential for haploinsufficient genes, which require biallelic expression
Abstract Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a rare, progressive lung disease that predominantly affects women. LAM cells carry TSC1/TSC2 mutations, causing mTORC1 hyperactivation and uncontrolled cell growth. mTORC1 inhibitors

Abstract Cell-free genetically encoded biosensors have been developed to detect small molecules and nucleic acids, but they have yet to be reliably engineered to detect

Abstract The DNA-repair capacity in somatic cells is limited compared with that in germ cells. It has remained unknown whether not only lesion-type-specific, but overall
Abstract Pancreatic islets control glucose homeostasis by the balanced secretion of insulin and other hormones, and their abnormal function causes diabetes or hypoglycaemia. Here we
Highlights Summary Using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to understand the mechanisms of neurological disease holds great promise; however, there is a lack of well-curated
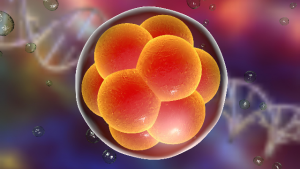
Highlights Summary At the moment of union in fertilization, sperm and oocyte are transcriptionally silent. The ensuing onset of embryonic transcription (embryonic genome activation [EGA])
Abstract The notion that mobile units of nucleic acid known as transposable elements can operate as genomic controlling elements was put forward over six decades
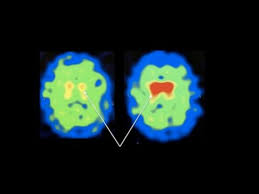
Abstract Progressive degeneration of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra is a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Dysregulation of developmental transcription factors is implicated

Abstract Aging is associated with complex molecular and cellular processes that are poorly understood. Here we leveraged the Tabula Muris Senis single-cell RNA-seq data set
Abstract During female germline development, oocytes become a highly specialized cell type and form a maternal cytoplasmic store of crucial factors. Oocyte growth is triggered
The 2010s brought major advancements in every aspect of the life sciences and ushered in an era of collaboration and multidisciplinary approaches. The Scientist spoke
A study of nematode worms, mice, and humans indicates that, across the animal kingdom, with aging comes more neural activity and when this natural increase

ABOVE: A healthy adult bimaternal mouse with offspring of her own LEYUN WANG Mice with same-sex parents In research published in October in Cell Stem
Immune cells function by recognizing pathogens and initiating a complex cellular response to mount a defense. People can show a wide range of genetically driven

Psychiatric disorders display common patterns of gene expression, according to a study published today (February 8, 2018) in Science. Researchers have analyzed transcripts within the
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate gene expression by inducing mRNA decay. But miRNAs can be regulated through other RNAs and DNA that bind and sequester them without

Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have attracted growing attention in recent years, but their function in living organisms has long remained a mystery. Now, researchers report that
Some big ideas seem to appear out of nowhere, but in 2008 Chuan He deliberately went looking for one. The US National Institutes of Health
Highlights • Fasting mimicking diet induces prenatal-development gene expression in adult pancreas • FMD promotes Ngn3 expression to generate insulin-producing β cells • Cycles of
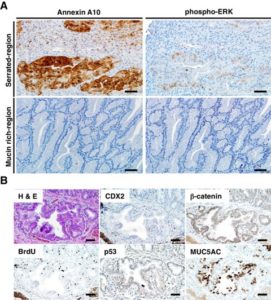
While 20–30% of colorectal cancers (CRCs) may arise from precursors with serrated glands, only 8–10% of CRCs manifest serrated morphology at diagnosis. Markers for distinguishing
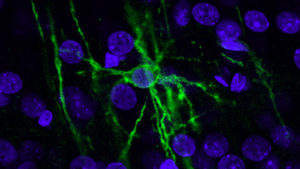
Neurodegenerative diseases are often associated with aging. To learn what happens within the aging brain and potentially gain information relevant to human health, researchers examined
Over the next decade, researchers will compile a comprehensive and freely available map of the cells of the human body, complete with descriptions about their
Transcription factors have long been viewed as “undruggable” targets for therapy: however, this concept may now need some tweaking. Cho et al. found that a
A synthetic genetic circuit that mimics the quorum-sensing systems used by bacterial populations to coordinate gene expression enables bacteria to deliver drugs to mouse tumours
Created by ePubSystems. Contact Us for similar site for your university or institute.